AMERICA’S NUMBER ONE SOURCE FOR CHRONIC NECK PAIN? WHIPLASH INJURIES
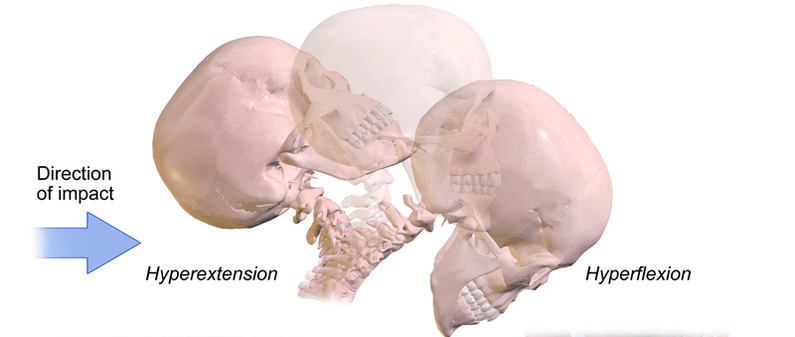
There are lots of reasons that people end up with acute neck pain — they have “Text Neck,” they worked out too hard, they slept wrong, they have poor posture, etc, etc, etc. This is a wholly different animal than CHRONIC NECK PAIN — neck pain that’s lasted at a minimum of months, and often times for years. After two and a half decades in practice, I’m convinced that the number one cause of chronic neck pain is WHIPLASH INJURIES from MOTOR VEHICLE ACCIDENTS or OTHER CAUSES. It’s not a reach once you see how many accidents there are (below), and how many people progress to chronic symptoms without ever completely healing (HERE).
For instance, Medline Plus (Neck Injuries and Disorders) says of neck pain, “Any part of your neck – muscles, bones, joints, tendons, ligaments, or nerves – can cause neck problems. Falls or accidents, including car accidents, are a common cause of neck pain.” A 2009 position paper by the IASP (International Association for the Study of Pain) said, “Neck pain is a common global problem, at least in the industrialized world, and it constitutes an important source of disability. Neck pain affects 30–50% of the general population annually.“
According to the American Academy of Pain Medicine, “severe headache or migraine pain (15%), neck pain (15%) and facial ache or pain (4%)” are some of the leading causes of pain in America (HERE). Furthermore, “Almost 59% reported an impact on their overall enjoyment of life, 77% reported feeling depressed, 70% said they have trouble concentrating, 74% said their energy level is impacted by their pain, and 86% reported an inability to sleep well.” And as for how many MVA’s there are here in America, USA Coverage (How Many Driving Accidents Occur Each Year?) says, “The most common question in issues involving vehicular fatalities is how many driving accident occur each year? If it’s all summed up in a yearly basis,there are 5.25 million driving accidents that take place per year. Statistics show that each year, 43,000 or more of the United States’ population die due to vehicular accidents and around 2.9 million people end up suffering injuries.” But these statistics don’t really tell the whole story.
Fetterman and Associates (How Many Car Accidents Occur Per Year?) reveal on their website that, “The most up-to-date information currently available only extends to 2012, and is provided by the Bureau of Transportation Statistics. In 2012, there were an estimated 5,615,000 highway accidents. But that number does not include accidents that occur in neighborhoods or parking lots. Highway accidents are easier to track. Some estimates of total accidents including the more minor ones are as high as 10 million per year.” But even this is not presenting the entire picture. Less than two years ago, Consumer Reports (14 Million Americans Were Involved in Accidents with Senior Drivers this Past Year) said that, “Over the past year, 14 million Americans aged 18 to 64 were estimated to be involved in accidents caused by drivers aged 65 and over.” It’s almost like every study and statistic that comes out is worse than the one that came out before it.
WHIPLASH PREVENTION
WHAT CAN YOU DO TO MAKE SURE YOU DO NOT BECOME A WHIPLASH STATISTIC?

While there are lots of things that certainly make whiplash injuries worse (HERE), likewise, there are a few things you can do to try and keep from becoming a whiplash statistic — one of the people who enters the world of CHRONIC PAIN through the door labeled “Whiplash”.
- HEAD RESTRAINT ADJUSTED PROPERLY: This is the inarguable #1, with tons of information found on this topic online, much of it in the form of peer-review. Without going in to great detail, make sure that the middle of your head restraint is even with your ear. Part of the problem is that many people keep their head restraints all the way down, allowing it to act as a fulcrum as the head is forced over it in the the event of a rear end collision. Be aware that studies have shown that most (over 85%) head restraints are positioned improperly.
- SEAT POSITIONED PROPERLY: Keep the seat in a relatively upright position. This has become a bigger deal in recent years, with younger people wanting to recline their seats.
- DRIVE A SAFER CAR: It seems like year in and year out, the safest cars are made by Volvo and Saab (not that I own or promote either brand). It is also important to remember that the smaller the vehicle you drive, the greater the chance of all injuries, including whiplash. Make sure to check out the various safety features and safety ratings before buying.
- PREPARE FOR THE REARENDER IN ADVANCE: I get it; you can never completely prepare to get rearended. However, if you hear brakes squalling, rather than first looking in the mirror or turning your head to look (whiplash is much worse in side impacts or if the head is turned at impact), plaster your back and head to your seat back and head restraint. If the head and neck don’t move (whip) on impact, there is no tearing of soft tissues in the neck
- SEAT BELTS: While seat belts unarguably save lives, they do not prevent or even reduce whiplash. A similar thing can be said of airbags. While I am a fan of airbags (I will forever have the scars from the “rug” burns on the insides of my arms from THIS CRASH), airbags will not help you out in a rear-ender type accident. They will, however, help in front end collisions.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU ARE INJURED IN A WHIPLASH TYPE OF ACCIDENT
Google “What to do after a car crash” and you will find about a million articles (many are little more than glorified ads) from attorneys, insurance companies, chiros, and therapists, all telling you that they know exactly what you need. Maybe they do, maybe they don’t — that’s for you to decide. Bottom line, if you need to go to the Emergency Department, do it. As long as there is no blood and guts, herniated discs, or broken bones, don’t expect doctors to find much, mainly because THESE SORTS OF INJURIES don’t show up very well with standard imaging tests such as MRI. There are, however, some simple concepts I feel are critical for you to understand to better deal with Whiplash Injuries.
- HOW LONG DOES IT TAKE INJURED SOFT TISSUES TO HEAL? I answer this question in my COLLAGEN SUPER PAGE. The bottom line here is that current peer-review shows that although the first phases of healing only take about three weeks, the final phase — the part where the Scar Tissue is strengthened and remodeled — can take two years or more. If you don’t know this, I promise that insurance companies will use it against you.
- WHAT IS PHASE I OF TREATING PEOPLE WITH WHIPLASH INJURIES? HERE is Phase I of treating Whiplash Injuries. Way too often people are bypassing Phase I and going straight to Phase II.
- WHAT IS PHASE II OF TREATING PEOPLE WITH WHIPLASH INJURIES? PHASE II of dealing with whiplash-induced soft tissue injuries is the focus of the majority of treatment plans. Unfortunately, the final aspect of Phase II — dealing with FHP — is rarely addressed (HERE).
The end result of either of the latter two bullets is people who frequently do great with adjustments. For a very short time. Often times just a day or two. Or maybe only an hour or two. If you want to see what makes a visit to my clinic different, take a look at THIS SHORT POST. As I have talked about at length in the past (HERE is one example), my goal is always to help you ASAP, as opposed to long and drawn out treatment schedules.
